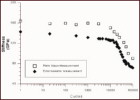
Extension in Composites This research focuses on the characterization of matrix damage in metal matrix composites under transverse loads. A volume integral equation method (VIEM) developed as a new numerical scheme for the solution of elastodynamic and elastostatic problems in unbounded solids containing multiple inclusions and cracks is used to investigate the mechanics of the damage evolution in a unidirectional SiC/Ti composite under transverse loading. The objective of this research is to analyze and predict the failure and fracture behavior in SiC/Ti composites, and to characterize the defects through NDE and determine the materials degradation in SiC/Ti metal matrix composites.
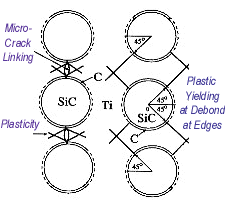
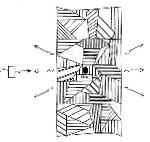
Failure Mechanism Diagram
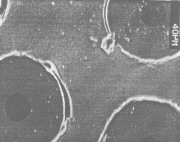
SEM Photomicrograph