An alternative discounting method is absolute
discounting,14.15 in which a constant value 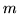 is subtracted from each
count. The effect of this is that the events with the lowest counts
are discounted relatively more than those with higher counts. The
discount coefficient is defined as
is subtracted from each
count. The effect of this is that the events with the lowest counts
are discounted relatively more than those with higher counts. The
discount coefficient is defined as
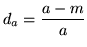 |
(14.16) |
In order to discount the same amount of probability mass as the
Good-Turing estimate, 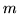 must be set to:
must be set to:
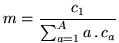 |
(14.17) |
Back to HTK site
See front page for HTK Authors
![]() must be set to:
must be set to: