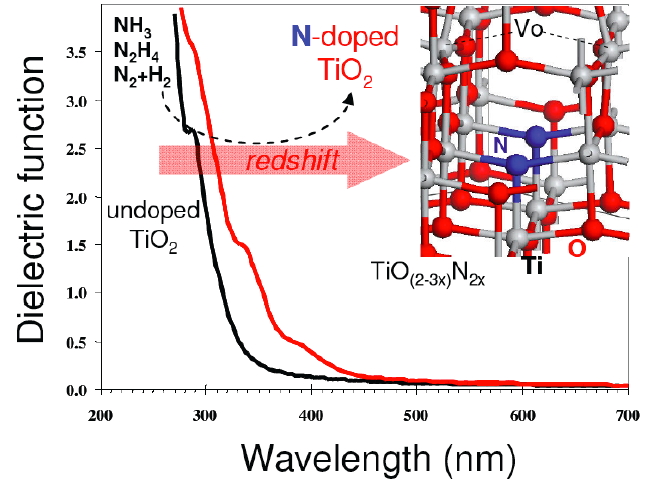
A key reaction of interest in the photocatalytic dissociation of water in hydrogen and oxygen, that yields clean fuel. The role of semiconductor is to absorb light, producing excitons, which dissociates into holes and electrons. The charge carriers then migrate to the surface or to a co-catalyst where the water oxidation reaction takes place. We use first-principle calculations to rationalize catalyst design. Besides band-gap, first-principles calculations allow us to determine the dielectric constant and the charge carrier mobility, which are key properties for a good dissociation of the exciton and migration of charges towards the catalytic sites. Several semiconductors have been studied (TiO2, Ta3N5, C3N4, …) and doping strategies are considered.